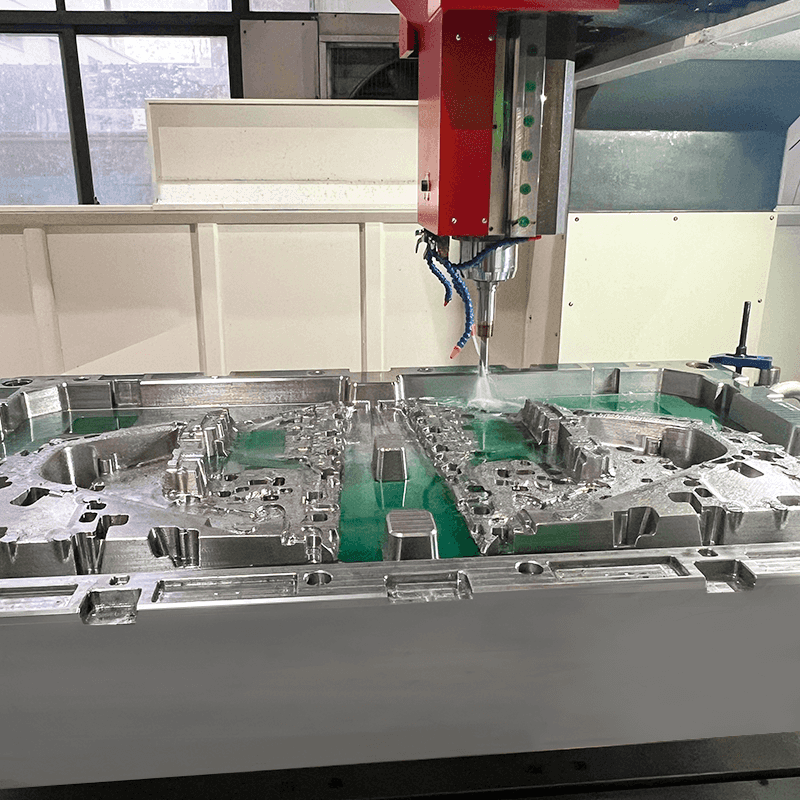
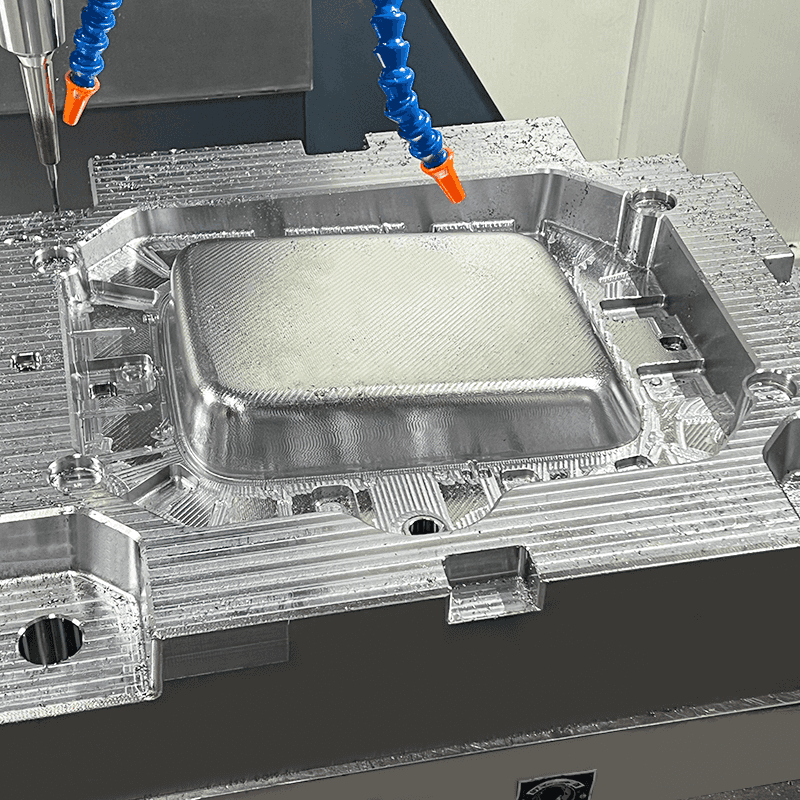
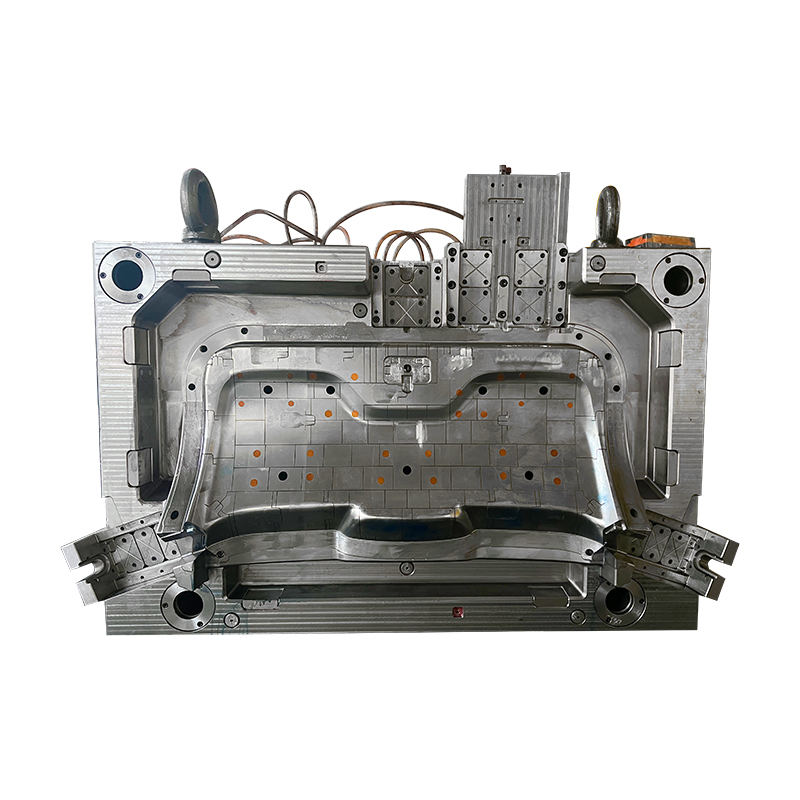
The world of thermoset plastics is vast and varied, offering numerous molding techniques tailored to specific materials and applications. Among these, phenolic injection molding, BMC compression molding, and BMC injection molding stand out due to their distinct processes and advantages.
Phenolic Injection Molding
Phenolic injection molding is a widely used process for producing parts from phenolic resins, a type of thermoset polymer known for its good mechanical properties and heat resistance. Phenolic resins, or phenolics, are synthesized from phenol and formaldehyde and are characterized by their rigidity, dimensional stability, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and electrical conductivity.
Process Overview
The phenolic injection molding process begins with the preparation of phenolic resin, which is often in a powdered form. The resin is heated and melted in the injection molding machine, transforming it into a viscous liquid. This liquid is then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once inside the mold, the resin undergoes a curing process, facilitated by heat and pressure, which causes it to solidify and take the shape of the mold cavity.
Advantages
Phenolic injection molding offers several advantages:
High Heat Resistance: Phenolic parts can withstand high temperatures without losing their structural integrity, making them ideal for automotive and industrial applications.
Electrical Insulation: Phenolics are good electrical insulators, suitable for electrical and electronic components.
Chemical Resistance: These materials resist corrosion from chemicals, adding to their durability.
Dimensional Stability: Phenolic parts maintain their shape and size even under varying environmental conditions.
Applications
Phenolic injection molding is commonly used to manufacture components such as electrical connectors, automotive parts, appliance housings, and industrial equipment components. Its ability to produce intricate and high-strength parts makes it a valuable technique in many sectors.
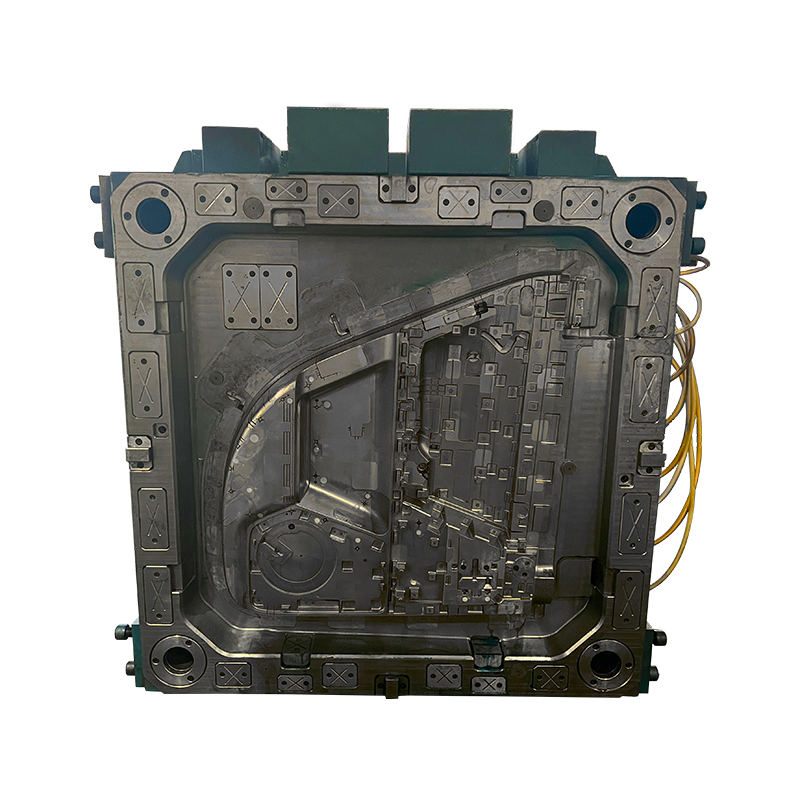
BMC Compression Molding
Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) compression molding is another prevalent method for shaping thermoset materials. BMC consists of a mixture of unsaturated polyester resin, glass fibers, and various additives, providing a robust and versatile material for various applications.
Process Overview
In BMC compression molding, the BMC material is placed into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed and subjected to high pressure, causing the BMC to flow and fill the cavity. Heat and pressure are maintained until the material cures, resulting in a solid, molded part. This process can produce large and complex parts with high precision.
Advantages
BMC compression molding has several benefits:
High Strength and Durability: The incorporation of glass fibers enhances the mechanical strength and durability of the molded parts.
Good Surface Finish: BMC parts often have a smooth and high-quality surface finish, suitable for aesthetic applications.
Dimensional Accuracy: The process provides high dimensional accuracy, essential for precision parts.
Versatility: BMC can be molded into a wide range of shapes and sizes, accommodating various design requirements.
Applications
BMC compression molding is used in producing automotive components, electrical enclosures, appliance parts, and various industrial components. Its ability to produce high-strength and high-precision parts makes it a preferred choice in many industries.
BMC Injection Molding
BMC injection molding shares similarities with phenolic injection molding but uses BMC material instead of phenolic resins. This process combines the benefits of injection molding with the advantageous properties of BMC.
Process Overview
The BMC injection molding process involves feeding the BMC material into an injection molding machine, where it is heated and melted. The molten material is then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. Similar to compression molding, the BMC undergoes curing in the mold, solidifying into the desired shape.