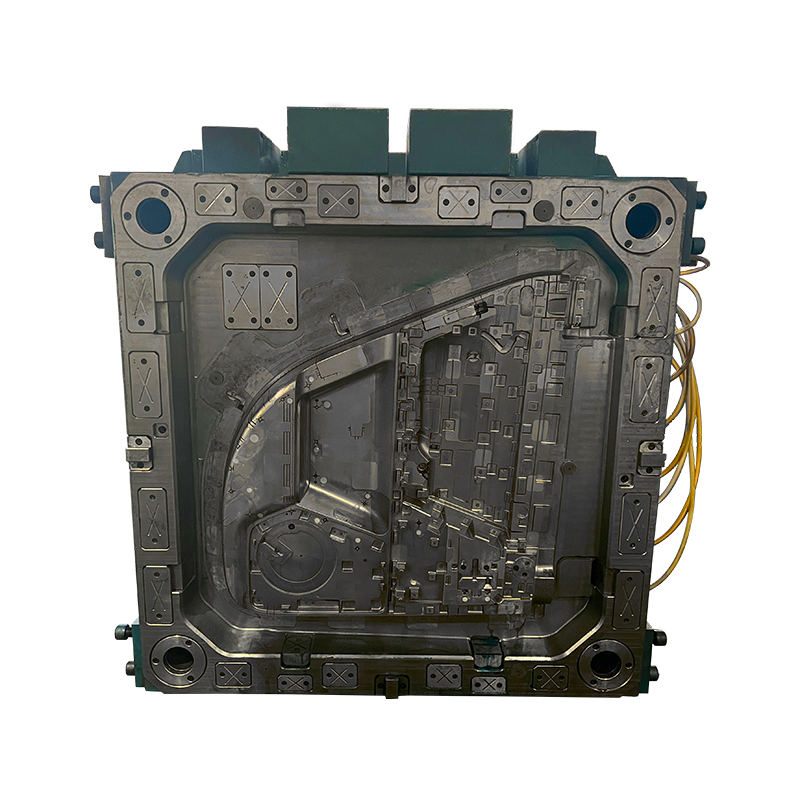
Plastic molds play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of essential everyday items such as tissue boxes and storage boxes. Each type of mold is meticulously designed to meet specific functional and aesthetic requirements, ensuring durability, functionality, and cost-effectiveness in their respective applications.
Plastic Tissue Box Mould
Plastic tissue box molds are engineered to produce containers that hold tissue papers, providing convenience and accessibility in homes, offices, and public spaces. These molds are typically made from durable materials such as steel or aluminum, selected for their thermal conductivity, strength, and resistance to wear.
Characteristics of Plastic Tissue Box Mould
Design Precision: Tissue box molds incorporate intricate cavities and ejector systems to mold tissue box components with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Material Compatibility: These molds accommodate various types of thermoplastic resins, including polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE), known for their flexibility, impact resistance, and ease of molding.
Surface Finish: Molds undergo surface treatments such as polishing and coating to enhance part release and improve the aesthetic appeal of molded tissue boxes.
Applications of Plastic Tissue Box Mould
Plastic tissue box molds find application in:
Household use for storing and dispensing tissues conveniently.
Commercial environments such as hotels, restaurants, and healthcare facilities.
Retail settings where branded or customized tissue boxes are marketed.
Storage Box Mould
Storage box molds are designed to manufacture durable containers used for organizing and storing various items in homes, offices, warehouses, and industrial settings. These molds are engineered to withstand the pressures and demands of molding large, sturdy containers with consistent wall thickness and structural integrity.
Characteristics of Storage Box Mould
Material Selection: Storage box molds are typically crafted from robust materials like steel or reinforced aluminum to endure high injection pressures and temperature variations.
Structural Design: Molds feature multiple cavities, core inserts, and cooling channels to facilitate efficient material flow, rapid cooling, and uniform part formation.
Customization Options: Manufacturers can customize storage box molds to produce containers of different sizes, shapes, and configurations to meet diverse customer needs.
Applications of Storage Box Mould
Storage box molds serve diverse applications:
Residential storage solutions for organizing household items, toys, and seasonal decorations.
Industrial storage bins and crates for logistics, warehouse management, and inventory control.
Commercial storage systems in retail stores, offices, and manufacturing facilities.
Manufacturing Processes
Both plastic tissue box molds and storage box molds undergo similar manufacturing processes, starting with mold design and engineering. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create detailed mold specifications, considering factors such as part geometry, material flow, and cooling efficiency. Advanced machining techniques such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) are employed to fabricate mold components with high precision and accuracy.
Once the mold components are fabricated, they undergo rigorous assembly and testing to ensure proper functionality and alignment. Surface treatments such as polishing, texturing, or coating are applied to enhance mold durability, improve part release, and achieve desired surface finishes in molded products.
Plastic tissue box molds and storage box molds represent critical components of the manufacturing ecosystem, enabling efficient production of essential storage and organizational solutions for diverse applications. As industries continue to innovate and expand, the role of plastic molds in shaping everyday products remains fundamental to enhancing convenience, functionality, and sustainability in modern living and working environments.