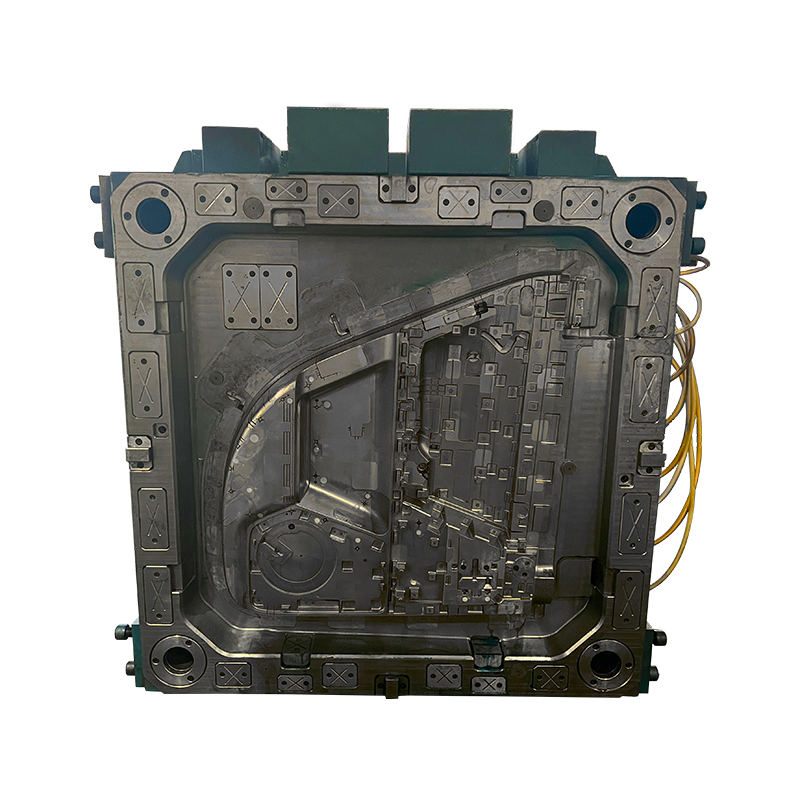
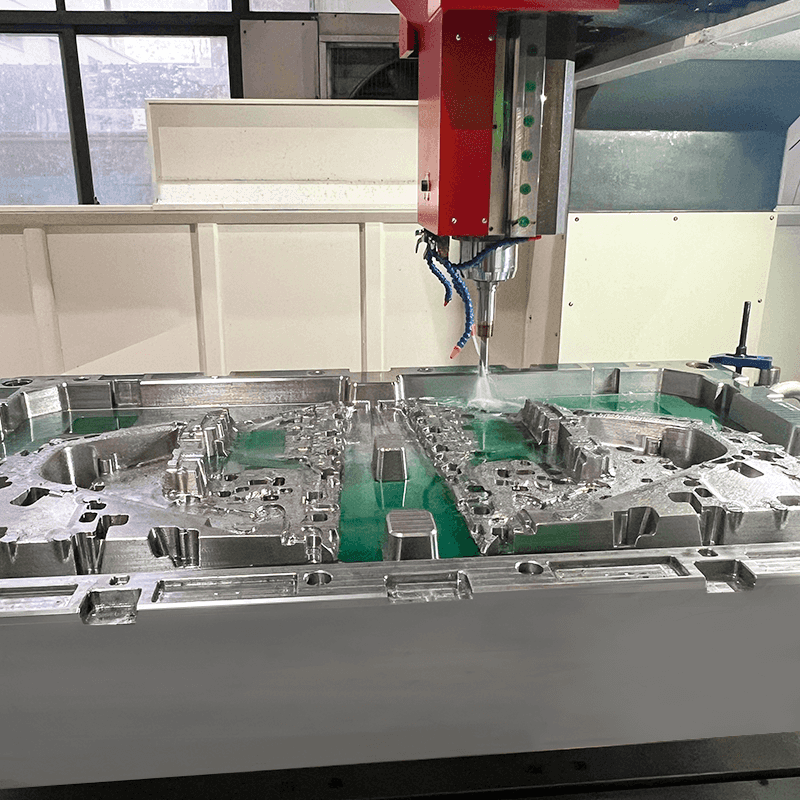
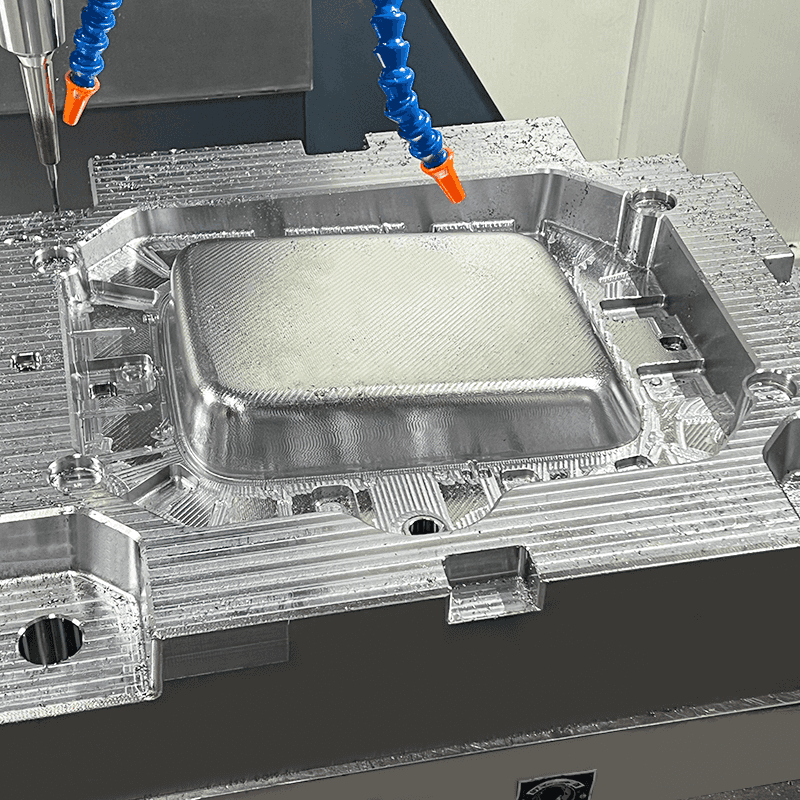
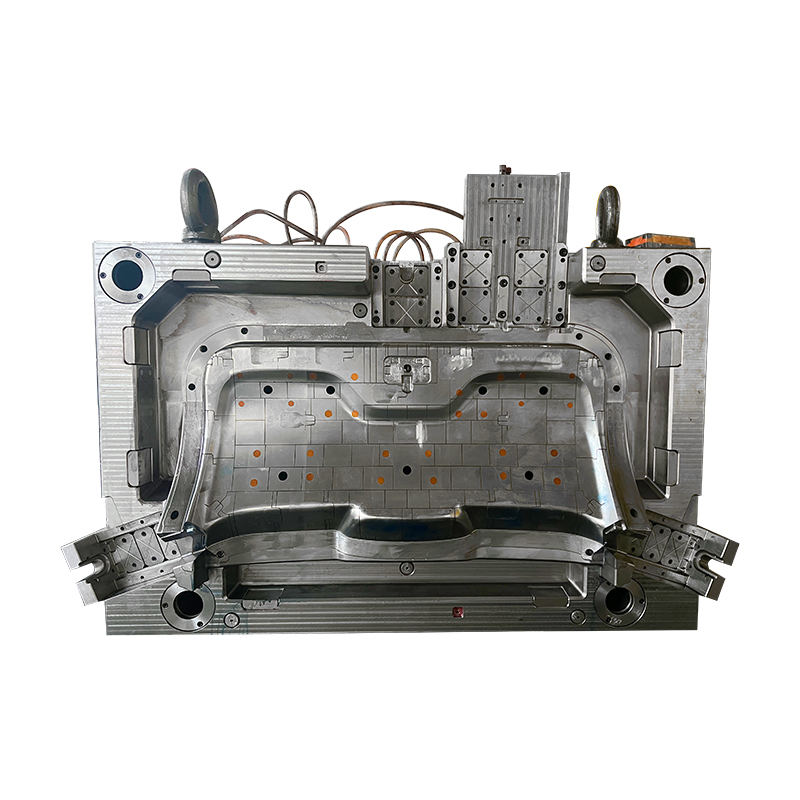
Compression moulds are fundamental to the press molding process, which is essential for producing a wide array of plastic products. These moulds are designed to withstand high pressure and heat, making them a core element in the compression molding technique. Let’s explore the crucial aspects of compression moulds, their design principles, and structural features.
The Role of Compression Moulds in Press Molding
Compression moulding involves heating a plastic material until it becomes soft and pliable. This material is then placed into a preheated mould where it is compressed under pressure to achieve the desired shape. Compression moulds are vital in this process because they shape the material and ensure consistency in product quality.
One of the primary roles of compression moulds is to provide precise control over the material flow and shape. They are designed to handle the high temperatures and pressures used in the press molding process. The moulds must be durable and able to withstand repeated use without degrading.
Design Principles of Compression Moulds
The design of compression moulds is critical to their performance. Several factors influence their design:
*Material Selection: Compression moulds are typically made from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the process.
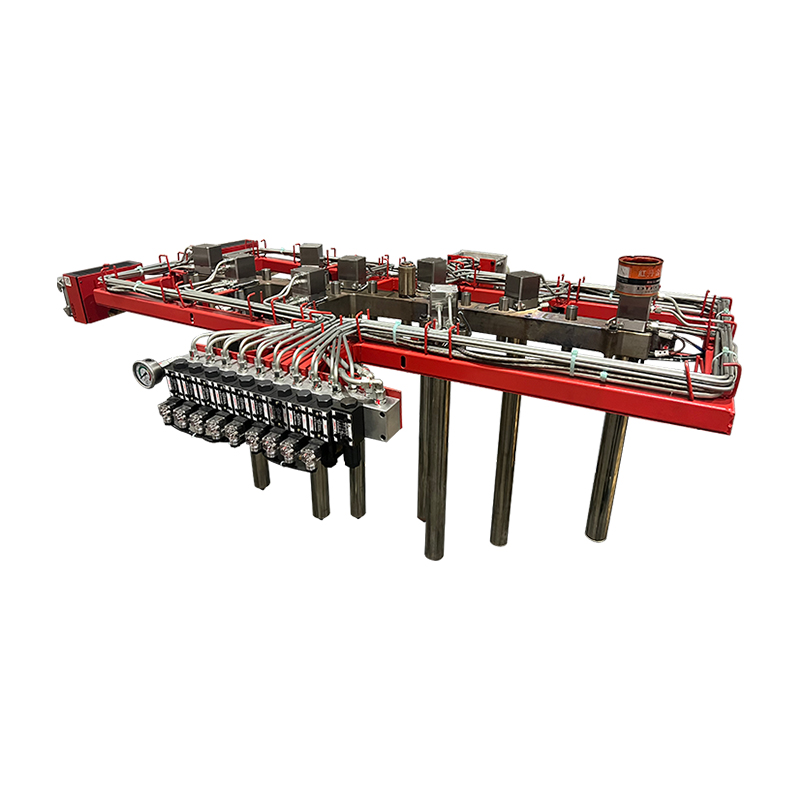
*Thermal Management: Effective heat transfer is essential in compression moulding. The design of the mould must include features for efficient heat distribution and cooling. This often involves incorporating cooling channels within the mould to maintain the required temperature throughout the process.
*Precision Engineering: The mould must be engineered to exact specifications to ensure that it produces accurate and consistent parts. This includes precise machining and alignment of mould components to avoid defects.
Structural Features of Compression Moulds
Compression moulds have several key structural features that enhance their performance:
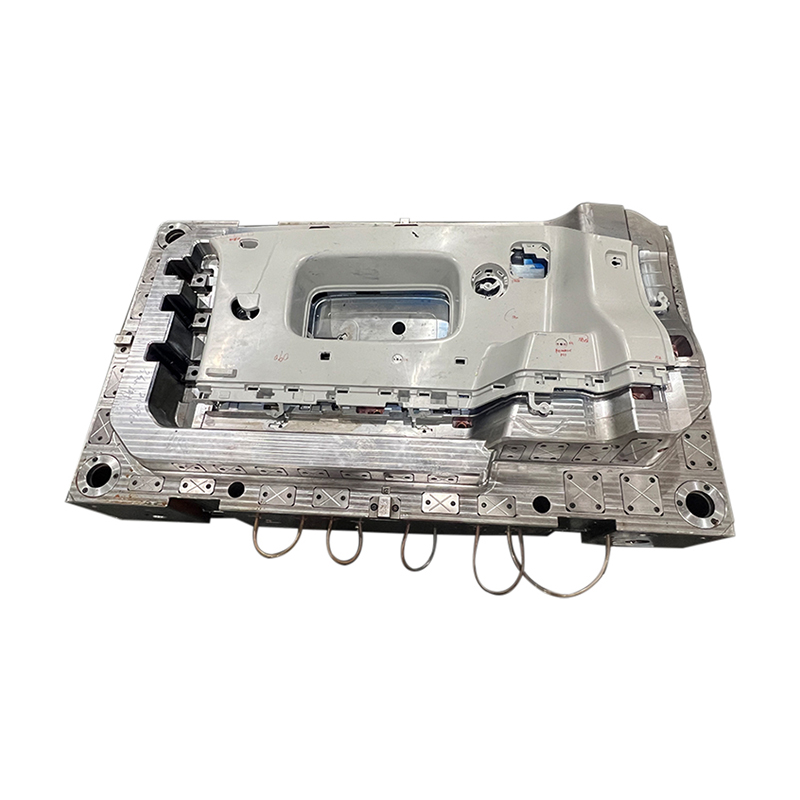
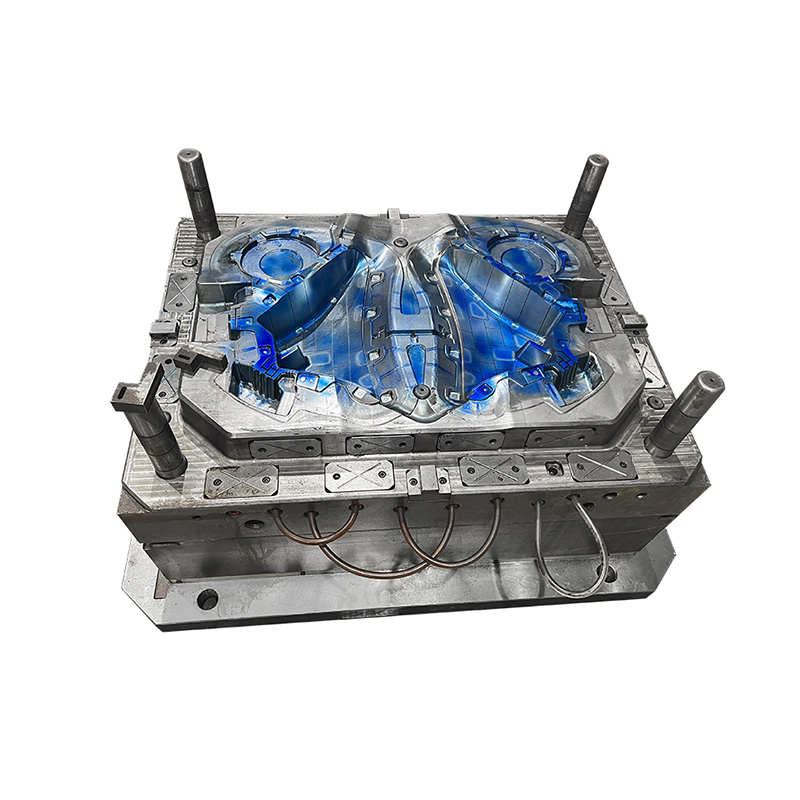
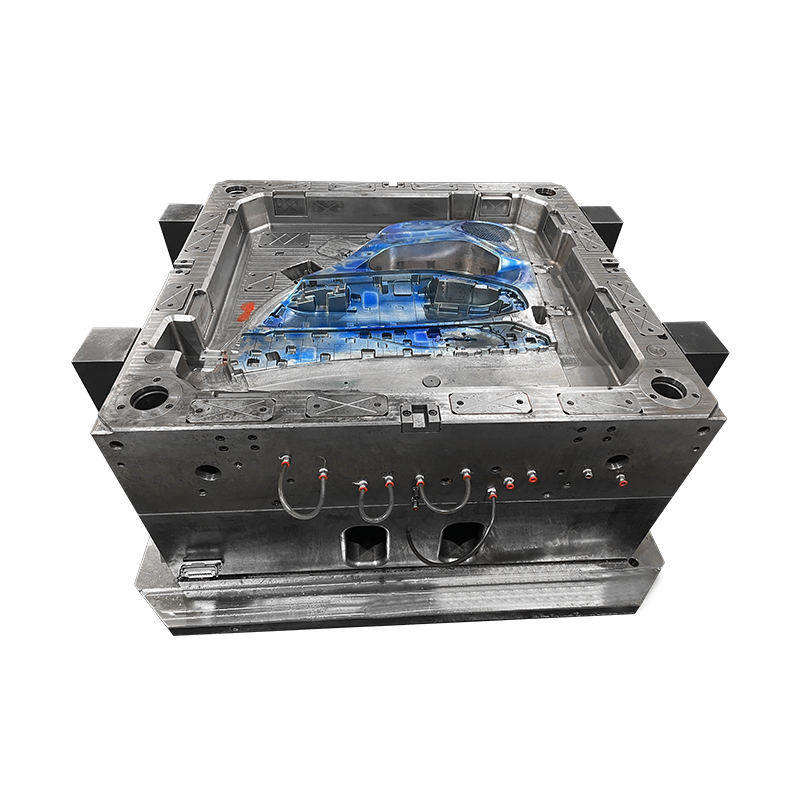
*Cavity and Core: The mould is divided into two main parts—the cavity and the core. The cavity is the part of the mould that shapes the exterior of the product, while the core shapes the interior. Both components must fit together perfectly to produce high-quality products.
*Ejector System: After the material has cooled and solidified, the finished product must be ejected from the mould. An ejector system, which often includes pins or plates, is used to push the product out of the mould cavity without causing damage.
*Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial in preventing air pockets and ensuring that the mould fills completely. Venting systems are incorporated into the mould design to allow trapped air to escape during the compression process.
Benefits of Using Compression Moulds
Compression moulds offer several benefits in press molding:
*High Efficiency: The design of compression moulds allows for rapid and efficient production, which is ideal for high-volume manufacturing.

*Consistent Quality: By maintaining precise control over material flow and temperature, compression moulds ensure consistent product quality.
*Durability: Made from robust materials, compression moulds are built to withstand the rigors of the molding process, providing long-term reliability.
Compression moulds play a crucial role in the press molding process, offering durability, efficiency, and precision. Their design and structural features are tailored to meet the demands of high-pressure and high-temperature molding, making them an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.